在本文中,我列出了十個我過去沒用過的html5功能,但現在發現它們很有用,廢話不多說,讓我們開始吧。
detais 標簽
<details>標簽向用戶提供按需查看詳細信息的效果。如果需要按需向用戶顯示內容,簡單的做法就是使用此<details>標簽。默認情況下,它是收起來的,打開后,它將展開并顯示被隱藏的內容。
事例:
<details>
<summary>Click Here to get the user details</summary>
<table>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Location</th>
<th>Job</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>Adam</td>
<td>Huston</td>
<td>UI/UX</td>
</tr>
</table>
</details>
運行結果:

技巧
在 GitHub Readme 中使用它來顯示按需的詳細信息。這是一個示例https://github.com/atapas/notifyme#properties

內容可編輯
contenteditable是可以在元素上設置以使內容可編輯的屬性。它適用于DIV,P,UL等元素。
注意,當在元素上沒有設置contenteditable屬性時,它將從其父元素繼承該屬性。
<h2> Shoppping List(Content Editable) </h2>
<ul class="content-editable" contenteditable="true">
<li> 1. Milk </li>
<li> 2. Bread </li>
<li> 3. Honey </li>
</ul>
運行結果:

技巧
可以讓span或div標簽可編輯,并且可以使用css樣式向其添加任何豐富的內容。這將比使用輸入字段處理它更好。試試看!
Map
HTML <map> 屬性 與 <area> 屬性一起使用來定義一個圖像映射(一個可點擊的鏈接區域)。可點擊的區域可以是這些形狀中的任何一個,矩形,圓形或多邊形區域。如果不指定任何形狀,則會考慮整個圖像。
事例:
<div>
<img src="circus.jpg" width="500" height="500" alt="Circus" usemap="#circusmap">
<map name="circusmap">
<area shape="rect" coords="67,114,207,254" href="elephant.htm">
<area shape="rect" coords="222,141,318, 256" href="lion.htm">
<area shape="rect" coords="343,111,455, 267" href="horse.htm">
<area shape="rect" coords="35,328,143,500" href="clown.htm">
<area shape="circle" coords="426,409,100" href="clown.htm">
</map>
</div>
運行結果:

技巧
map有其自身的缺點,但是你可以將其用于視覺演示。
mark 標簽
<p> Did you know, you can <mark>"Highlight something interesting"</mark> just with an HTML tag? </p>
運行結果:

技巧
可以使用css更改高亮顏色:
mark {
background-color: green;
color: #FFFFFF;
}
data-* 屬性
data-*屬性用于存儲頁面或應用程序專用的自定義數據。可以在 JAVAScript 代碼中使用存儲的數據來創建更多的用戶體驗。
data-*屬性由兩部分組成
- 屬性名不能包含任何大寫字母,并且必須在前綴“data-”之后至少有一個字符
- 屬性值可以是任何字符串
事例:
<h2> Know data attribute </h2>
<div
class="data-attribute"
id="data-attr"
data-custom-attr="You are just Awesome!">
I have a hidden secret! </div>
<button onclick="reveal()">Reveal</button>
在 JS 中:
function reveal() {
let dataDiv = document.getElementById('data-attr');
let value = dataDiv.dataset['customAttr'];
document.getElementById('msg').innerHTML = `<mark>${value}</mark>`;
}
**注意:**要在 JS 中讀取這些屬性的值,可以通過getAttribute('data-custom-attr')g來獲取,但是標準方式是用dataset來獲取。

技巧
你可以使用它在頁面中存儲一些數據,然后使用REST調用將其傳遞給服務器。
output 標簽
<output> 標簽表示計算或用戶操作的結果。
<form oninput="x.value=parseInt(a.value) * parseInt(b.value)">
<input type="number" id="a" value="0">
* <input type="number" id="b" value="0">
= <output name="x" for="a b"></output>
</form>

技巧
如果要在客戶端 JS 中執行任何計算,并且希望結果反映在頁面上,可以使用<output>,這樣就無需使用getElementById()獲取元素的額外步驟。
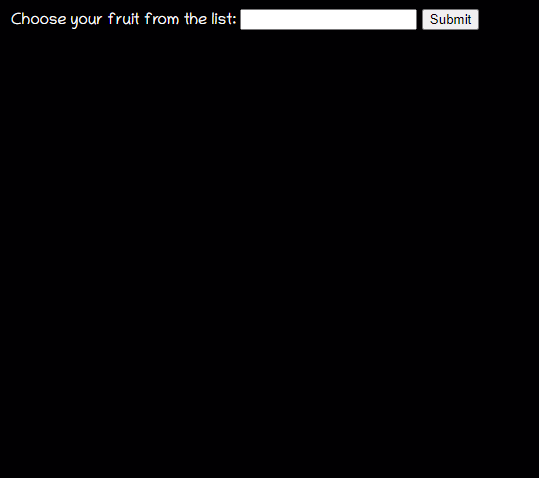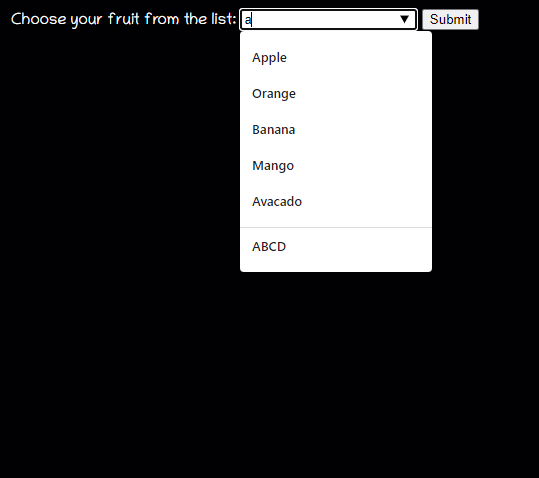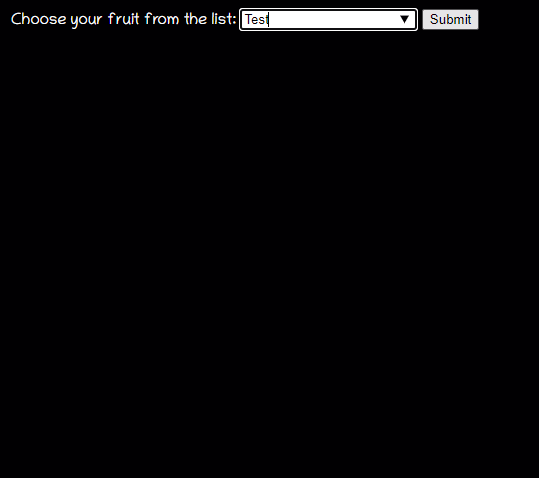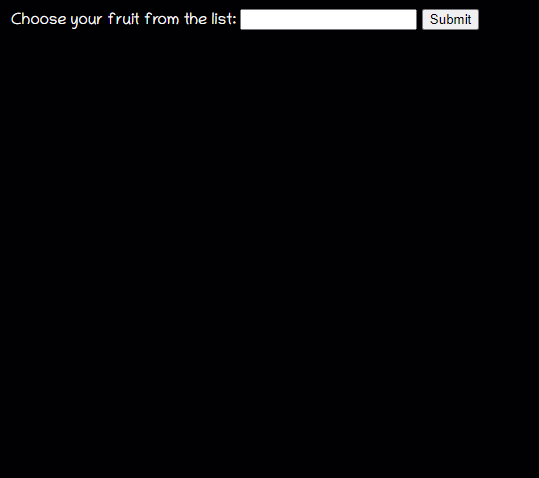
datalist
<datalist>元素包含了一組<option>元素,這些元素表示其它表單控件可選值.
事例:
<form action="" method="get">
<label for="fruit">Choose your fruit from the list:</label>
<input list="fruits" name="fruit" id="fruit">
<datalist id="fruits">
<option value="Apple">
<option value="Orange">
<option value="Banana">
<option value="Mango">
<option value="Avacado">
</datalist>
<input type="submit">
</form>
技巧
dataList的表現很像是一個select下拉列表,但它只是提示作用,并不限制用戶在input輸入框里輸入什么
select標簽創建了一個菜單。菜單里的選項通option標簽指定。一個select元素內部,必須包含一個option元素,
總的來說就是,它們都可以顯示出一個下拉表單框,但是select標簽只能在它提供的選項中選擇,而datalist不僅可以讓你選擇,還可以讓你自己輸入其它的選項。
Range(Slider)
range是一種 input 類型,給定一個滑塊類型的范圍選擇器。
<form method="post">
<input
type="range"
name="range"
min="0"
max="100"
step="1"
value=""
onchange="changeValue(event)"/>
</form>
<div class="range">
<output id="output" name="result"> </output>
</div>

meter
<meter>元素用來顯示已知范圍的標量值或者分數值。
<label for="home">/home/atapas</label>
<meter id="home" value="4" min="0" max="10">2 out of 10</meter><br>
<label for="root">/root</label>
<meter id="root" value="0.6">60%</meter><br>

技巧
不要將<meter>用作進度條來使用,進度條對應的<Progress> 標簽。
<label for="file">Downloading progress:</label>
<progress id="file" value="32" max="100"> 32% </progress>

Inputs
對于input標簽類型,最常見的有 text,password 等等,下面列舉一些比較少見的語法。
required
要求輸入字段必填。
<input type="text" id="username1" name="username" required>

autofocus
文本輸入字段被設置為當頁面加載時獲得焦點:
<input type="text" id="username2" name="username" required autofocus>
用正則表達式驗證
可以使用regex指定一個模式來驗證輸入。
<input type="password"
name="password"
id="password"
placeholder="6-20 chars, at least 1 digit, 1 uppercase and one lowercase letter"
pattern="^(?=.*d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{6,20}$" autofocus required>
Color picker
一個簡單的顏色選擇器。
<input type="color" onchange="showColor(event)">
<p id="colorMe">Color Me!</p>

作者:Ahmad shaded 譯者:前端小智 來源:sitepoint
原文:https://dev.to/atapas/10-useful-html5-features-you-may-not-be-using-2bk0