消息引擎的核心職責就是將生產者生產的消息傳輸到消費者,設計消息格式是各大消息引擎框架的關鍵問題,因為消息格式決定了消息引擎的性能和效率。本文帶大家探究消息引擎kafka當前所用的message格式是什么。
一、Kafka message format
kafka從0.11.0版本開始所使用的消息格式版本為v2,參考了 Protocol Buffer而引入了變長整型(Varints)和 ZigZag 編碼。Varints是使用一個或多個字節來序列化整數的一種方法,數值越小,其所占用的字節數就越少。ZigZag編碼以一種鋸齒形(zig-zags)的方式來回穿梭于正負整數之間, 以使得帶符號整數映射為無符號整數,這樣可以使得絕對值較小的負數仍然享有較小的Varints編碼值,比如-1編碼為1,1編碼為2,-2編碼為3。

kafka v0和v1版本的消息格式,如果消息本身沒有key,那么key length字段為-1,int類型的需要4個字節來保存,而如果采用Varints來編碼則只需要一個字節。根據Varints的規則可以推導出0-63之間的數字占1個字節,64-8191之間的數字占2個字節,8192-1048575之間的數字占3個字節。而kafka broker的配置message.max.bytes的默認大小為1000012(Varints編碼占3個字節),如果消息格式中與長度有關的字段采用Varints的編碼的話, 絕大多數情況下都會節省空間,而v2版本的消息格式也正是這樣做的。不過需要注意的是Varints并非一直會省空間,一個int32最長會占用5個字節(大于默認的4字節), 一個int64最長會占用10字節(大于默認的8字節)。
因為Kafka的message經歷過幾次的版本迭代更改,本文以v2版本為例講述。
二、Record Batch
在Kafka中,數據是按照topic和partition的方式進行組織和存儲的。每個partition的數據被分成一個或多個segment文件,并且每個segment文件包含若干個Record Batch。因此,Record Batch也是Kafka中重要的數據結構之一。
在Kafka中,Record Batch指的是一組相關的消息集合,它們具有相同的key、value類型和所屬的topic和partition。每個Record Batch包含若干條消息(Record),并且這些消息被順序地寫入到磁盤中,以提高讀取效率。
具體而言,Record Batch由以下幾部分構成:
Record Batch Header:包含了當前Batch的元數據,如Magic Code、Batch Size、First Offset等信息。
Record Header:每個Record都附帶有一個Header,用于描述該Record的元數據信息,例如時間戳、壓縮類型、CRC校驗值等。
Record Body:記錄具體的消息內容,包括Key、Value等字段。
需要注意的是,Kafka的Record Batch通常具有比較大的體積(默認大小為16KB),因此可以將多個相關的消息打包在一起進行傳輸和處理,從而提高了消息的傳輸效率和吞吐量。另外,Kafka還支持對Record Batch進行壓縮和批量操作,以進一步提高數據的傳輸效率和性能。
總的來說,Record Batch是Kafka中定義的一個重要數據結構,用于管理和組織消息,提高消息的讀寫效率和傳輸性能。
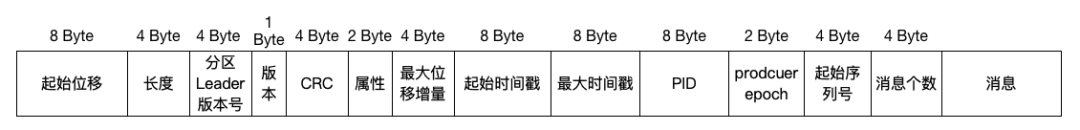
baseoffset: int64 標識當前的batch的起始偏移量
batchLength: int32 該batch的長度
partitionLeaderEpoch: int32 確保數據可靠性
magic: int8 魔法數字,當前為2,也即當前的message版本為v2版本
crc: int32 crc校驗
attributes: int16 消息屬性
bit 0~2: 是否壓縮和壓縮的格式
0: no compression
1: gzip
2: snAppy
3: lz4
4: zstd
bit 3: timestampType
bit 4: isTransactional (0 means not transactional)
bit 5: isControlBatch (0 means not a control batch)
bit 6: hasDeleteHorizonMs (0 means baseTimestamp is not set as the delete horizon for compaction)
bit 7~15: unused
lastOffsetDelta: int32 RecordBatch中最后一個Record的offset與first offset的差值
baseTimestamp: int64 第一條時間戳
maxTimestamp: int64 最大的時間戳,保證消息組裝時的正確性
producerId: int64 支持冪等性
producerEpoch: int16 支持冪等性
baseSequence: int32 支持冪等性,消息序號
records: [Record] Record個數
用以下圖表示 V2 版本消息批次的樣子:
三、Record
在Kafka中,Record Batch和Record是兩種不同的數據結構,但它們之間存在著緊密的關系。
Record是指Kafka中的一條消息,通常由Key、Value、Timestamp等字段組成。而Record Batch是指將多個相關的Record打包在一起進行傳輸和處理的數據結構,每個Record Batch通常包含若干條記錄,并且這些記錄具有相同的key、value類型和所屬的topic和partition。
具體來說,每個Record Batch中的Record都被依次存儲在一個連續的二進制數據塊中,每個Record包含自己的Header和Body部分。而Record Batch則包含了當前Batch的元數據信息和所有記錄的元數據信息,如Batch Size、First Offset、Last Offset、CRC校驗值等。
消息格式如下所示:
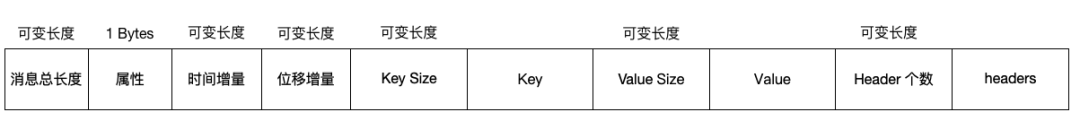
#消息長度
length: varint
#消息屬性
attributes: int8
# 時間戳增量
bit 0~7: unusedtimestampDelta: varlong
#偏移量增量
offsetDelta: varint
#key長度
keyLength: varint
#key值
key: byte[]
#value長度
valueLen: varint
#value值
value: byte[]
#header信息
Headers => [Header]
Record信息通過如下方式封裝
public static int writeTo(DataOutputStream out,
int offsetDelta,
long timestampDelta,
ByteBuffer key,
ByteBuffer value,
Header[] headers) throws IOException {
// 消息總數
int sizeInBytes = sizeOfBodyInBytes(offsetDelta, timestampDelta, key, value, headers);
ByteUtils.writeVarint(sizeInBytes, out);
// 屬性
byte attributes = 0; // there are no used record attributes at the moment
out.write(attributes);
// 時間增量
ByteUtils.writeVarlong(timestampDelta, out);
// 位移增量
ByteUtils.writeVarint(offsetDelta, out);
// key
if (key == null) {
ByteUtils.writeVarint(-1, out);
} else {
int keySize = key.remAIning();
// key size
ByteUtils.writeVarint(keySize, out);
// key
Utils.writeTo(out, key, keySize);
}
// Value
if (value == null) {
ByteUtils.writeVarint(-1, out);
} else {
int valueSize = value.remaining();
// value size
ByteUtils.writeVarint(valueSize, out);
// value
Utils.writeTo(out, value, valueSize);
}
// header
ByteUtils.writeVarint(headers.length, out);
for (Header header : headers) {
// header key
String headerKey = header.key();
byte[] utf8Bytes = Utils.utf8(headerKey);
// header key 長度
ByteUtils.writeVarint(utf8Bytes.length, out);
// header key 值
out.write(utf8Bytes);
// header value
byte[] headerValue = header.value();
if (headerValue == null) {
ByteUtils.writeVarint(-1, out);
} else {
// header value 長度
ByteUtils.writeVarint(headerValue.length, out);
// header value 值
out.write(headerValue);
}
}
return ByteUtils.sizeOfVarint(sizeInBytes) + sizeInBytes;
}
根據以上代碼邏輯,用以下圖表示 V2 版本消息格式的樣子:
四、總結
message(又稱record)總是分批寫入的。一批消息的技術術語是一個record batch:
- 一個record batch包含一個或多個record。
- 在退化的情況下,我們可以有一個包含單個record的record batch。
- record batch和record有它們自己的headers。